Memory Management
Table of Content
• What do you understand by the term Memory Management?
• The key function of Memory Management
• What is entailed by disintegration in Operating System?
• What does Swapping in Operating System stand for?
• What is known to be the Logical Address Space & Physical Address Space?
· Different types of Memory Management
• Cache Memory
• Meaning of Cache Memory
• What are dissimilar types of Cache Memory?
• What is understood by Virtual Memory in Operating System?
• What is called to be the Demand Paging?
• What is Memory Management in Operating Systems?
• Swapping and its Meaning
• Memory Allocation?
• What is Memory Heap?
• Elucidate Memory Management in C & C++
• Explain Linux Memory Management
• How to Deallocate Memory in C?
• Describe Computer Memory
• What do you get by Addressing Modes?
• Memory Card
• Memory Leak
• What is Memory Dump?
• Physical Memory in Operating System and its implication
• How to secure Memory Management Error?
• What is known to be the Contiguous Memory?
• Frequently Asked Questions
What is Memory Management?
The term Memory Management is recognized to be the way in the direction of commanding and contriving for the system memory and also aimed towards apportioning packets foreboded the blocks to dissimilar running projects in order to optimize the system process. This can take place in hardware, as well as in the operating system, in programs and applications.
In hardware, memory management admits some of the portions that actually store up information similar to RAM chips, memory cache, and the solid-state drives. In the OS, memory management admits the distribution of meticulous memory blocks to the individual projects as user demand for a transform. It can be very well seen that at the application level, memory management ensures the ease of access of suitable memory for the objects and information structures of each running system and that too at all considerations and there rest various facilities catered by memory management too.
It can be very well seen that the SCO OpenServer framework commits the inclusive set of memory administration instrument that puts up applications to have whole control over the expansion of their address space as well as appropriate for an extensive collection of operations on both process address spaces and the mixture of memory objects that dwells in the framework. The SCO Open Server memory-administration facilities admit:
1. Very much in use to draw together the framework's operations on memory.
2. Make available the set of essential part mechanisms to be forceful and satisfactorily general to hold up the custom of fundamental system services devoid of special kernel support.
3. Looking forward to maintaining steadiness with the current setting, purposely employing the UNIX document framework as the namespace for named virtual-memory objects.
Purpose of Memory Management
The standard reason behind memory management is to move forward with the RAM utilization. The primary requirement is to present the methods to more and more apportion parts of memory to programs at their best possible demand, and to make it free for recycling when did not really necessitated. This is known to be the critical process to any prompted PC framework where more than a single procedure may be in development.
Fragmentation in Operating System
Fragmentation serves to be the process wherein which the storage space gets applied unproductively by moving back its capacity or implementation or both. The accurate results of fragmentation swear by the scrupulous understanding of storage system being expended and the precise type of fragmentation. There remain three dissimilar yet associated types of fragmentation: external, internal, and data fragmentation which may be accessible in shelter or combination. Fragmentation is admitted in kind for enhancements in speed or smoothness.
External Fragmentation - External Fragmentation encounters when there stays a vibrant memory allocation algorithm that intends for some memory and a small part being left over that cannot be viably employed. When an unnecessary amount of external fragmentation comes about, the measure of usable memory gets fundamentally reduced. In this manner, the Total memory space survives to accomplish a demand, though it is not adjacent.
Internal Fragmentation: Internal fragmentation is recognized to be the space emaciated inside apportioned memory blocks in the outlook of incarceration on the granted sizes of assigned blocks. It can also be making out that the Allocated memory might be slightly superior to quested memory; this size contrast is memory internal to a segment, though not being used.
Data Fragmentation - Data fragmentation encounters when the compilation of data in memory is emitted in many parts that are not close to one another. In general, it is the outcome of striving to implant vast objects into storage that has at once lasted external fragmentation.
Swapping in Operating System
Swapping can be determined as the procedure or memory management process which gets used by means of the operating system in order to put up the use of the processor by actuating some barricaded procedure from the original memory to the auxiliary memory. Accordingly, composing a queue of the momentarily set aside process and the carrying out goes forward with the newly arrived process. Just after the swapping process gets complete, the OS experiences two alternatives in picking out a modus operandi for carrying out the process- Operating System can give up lately made process and operating system could ratify debarred process from the swap memory.
What do you understand by the Logical Address Space & Physical Address Space?
Address very well concerns about the location that stays in the memory. There are two types of addresses that are logical and physical address. Address produced by CPU when a program is running is adverted as Logical Address. This particular address is implicit as there is no physical subsistence. This address is used as a variety of standpoint to get to the physical memory area. When logical address gets created by programs and then is called as Logical Address Space.
One can very well make out that the Physical Address distinguishes for a physical area in a memory. Memory-Management Unit reads the physical address for the logical address as well. MMU applies unfailing address meting out a physical address. There can be very well seen that the client never deals with the physical address. A logical address is represented to the physical address by means of employing hardware and is foreboded as Memory-Management Unit. The physical address having to do with the consistent addresses in a Logical address space is predicted to be the Physical Address Space.
What comes out to be the diverse types of Memory Management?
Diverse memory management techniques are committed as follows:
· Single Adjoining Allocation – It can be made out that the single allotment is the smallest amount of difficult memory management strategy. Maximum memory can be accommodated for the operating system and is easy to get to the single application. MS-DOS serves to be a case of a structure which assigns memory all along these lines. There stays a great need to make out for a framework employing for the single conterminous task that may be at present multitask by switching the substance of memory to toggle among clients.
· Partitioned Allocation - Partitioned allocation keeps apart indispensable memory into plentiful memory sections, by and large, contiguous areas of memory. Memory management makes up of indicating a division to work when it starts out and un-allocating it when that task comes together. Partitioned assignation commands for few hardware support to go on the task of tampering with each other or with the OS. Unlike frameworks employed base and limits registers which comprised of the points of restriction of the packet as well as flagged unacceptable access. The UNIVAC 1108 Storage Limits Register had cut off base/headed sets for directions and information.
· Paged Memory Management - Paged memory sets apart the system's important memory into determined size units called up as page outlines and the program's virtual address space into pages of an analogous size. There can be very well understood that the physical memory can be attributed to a page principle while the address space seems adjoining. At this time, every task goes on campaigning in its personal address space. There has to be some single address space OS that runs all processes contained by a single address space, for example, IBM i, which runs all procedures in an enormous address space, and IBM OS/VS2 SVS, which ran all undertakings in a single 16MiB virtual address space.
· Segmented Memory Management - Segmented memory does not grant the client's program an undeviating and adjoining address space. It can be understood that the Segments are ambits of memory that on average speak about the logical grouping of data, for example, a coding technique or data selection. These sections want hardware support as a segment table, which in general holds back the physical address of the segment in memory, its size, and other information.
What is Cache Memory?
The Cache Memory is identified to be very close to the CPU. All current Instructions are preserved in the Cache Memory. It is lined up for the sake of holding open the data which is given by the client and is imperative for the CPU to practice a Task. The Capacity of the Cache Memory is less proportional to Memory and Hard Disk.
What is the significance of Cache Memory?
The cache memory requirement is for the reason that there is the principal memory and the CPU. As a result, apart from how speedy the processor is, the processing speed counts more on the velocity of the fundamental memory. The cache memory entrepots the program as of now being fulfilled or which might be performed surrounded by a succinct timeframe. The cache memory hives away transient information that the CPU may necessitate for control.
Different types of Cache Memory
· Level 1 (L1) Cache - It is also called as a primary cache. It is contained exclusively with the processor chip. Its small limit browses 8 Kb to 128 Kb.
· Level 2 (L2) Cache - This level is more sluggish than L1 cache. It can be very well understood that the storage limit deviates from 64 Kb to 16 MB. The present processors are full of highly developed transfer cache which is turned up on processor chip which is L2 type cache. The normal size of this cache ranges from 512 kb to 8 Mb.
· Level 3 (L3) Cache - This turns up break up from processor chip on the motherboard. It subsists on the PC that applies L2 advanced transfer cache. It is more tedious than L1 as well as L2 cache and its limit is up to 8 MB of L3 cache.
What is Virtual Memory in Operating System?
In swearing out, virtual memory is said to be a memory management system that is carried out employing both hardware and software. It functions for the memory addresses used by a program, foreboded Virtual Addresses, into physical addresses in PC memory. Principle Storage as discovered by a procedure or task comes out as a contiguous address space or an anthology of coterminous segments. The OS contends virtual address spaces and the undertaking of real memory to virtual memory. Address explanation hardware in the CPU regularly touched as a memory management unit naturally makes an interpreting of a virtual address to physical address.
Example of virtual memory is Virtual memory is on the whole carried out by demand paging. Similarly, it can be substantiated in a segment system. Demand segment can likewise be used to furnish virtual memory.
What is Demand Paging?
In an operating system, demand paging serves to be a technique for Virtual Memory Management. In a structure, that makes use of demand paging, the OS repeats a disk page into physical memory just if an attempt is made to right to use it and that page is not as of now in memory. It follows that a procedure bugs out the execution with none of its pages in physical memory, and many page error will occur in anticipation of the superior part of a procedure's acting upon a set of pages is located in physical memory. This is a case of a lazy stacking method.
What is Memory Management in Operating Systems?
In an operating system, memory management serves to be the capacity in charge of carrying on with the system's Primary Memory. The memory management supervises the standing of every memory area, either doled out or free. It makes up one's mind as to how memory is delegated among dealing forms, preferring which gets memory, when they latch on, and the amount they are tolerated. At the point when memory is apportioned, it very well figures out which memory areas will be allowed. It tracks when memory is released or unallocated and raises the status.
What is Swapping?
This is known to be a procedure that should be in memory for implementation. Yet, some of the time there stays an inadequate main memory to clutch all the active processes in a timesharing framework. The abundance processes are on disk as well as gained to run vigorously. Swapping is the way of bringing every process in main memory that runs it for some time and after that bringing back to the disk.
What is Memory Allocation?
Memory Allocation is the best possible way toward adjusting segments of memory in a program which demands to be employed so as to stock up variables, as well as examples of structures and classes. In solitary partition memory allocation, operating system occupies in lower memory while user processes implement in higher processes. Other than, in multiple partition memory, memory is shared out into an assortment of fixed size partition. Operating system engrosses fixed components and other portions of main memory are for user processes. There are two original types of memory allocation:
Static Memory - Static memory apportionment is in the habit to announce for a variable or the case in point of structure or class. The memory is apportioned by an operating system. The name which we speak out of the object could be employed to contact the memory block.
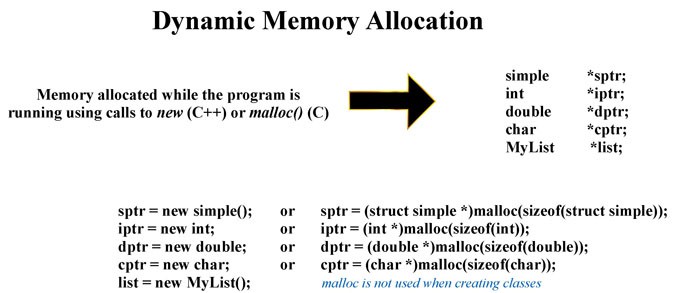
Dynamic Memory - When we employ dynamic memory allocation we boast the OS assign a block of memory of the correct size when the program is campaigning. This is done either with the new malloc function. This block of memory is doomed and a pointer to the block is brought back. After that, this is preserved in a pointer to the definite data type.
What is Memory Heap?
The Heap is said to be that piece of system memory that is apportioned to a running application, where memory could be dealt out for the variables, class, instance etc. It is given that a pointer to any of the apportioned block, the OS can appear in either way to hit upon the block adequately and it comes out to be enormous enough to block up a go-ahead memory allocation. It can be made out realized that the blocks that are apportioned on the heap are extraordinary data structure that comprise of (1) A pointer to the end of the past block, (2) a pointer to the end of this block, (3) the apportioned block that may transform in size reliant upon its consumption, (4) it is said to be a pointer to the set up of this block, and (5) a pointer to the accompanying block.
Clarify Memory Management in C & C++
More than a few functions can be expended for memory allocation in C like malloc, calloc, realloc, free. In C, the right size of an array is difficult to understand until it accumulates time, i.e., the time when a compiler piles up the code in C language. Dynamic memory allocation allows the program to obtain more memory space while campaigning or let go it if it's not demanded. In dynamic memory allocation, memory space can be manually handled for a program. the malloc() apportions the called for the size of bytes as well as generates for a pointer first byte of apportioned space calloc() allocates space for the collection constituents, initialize it to zero and subsequently that returns the pointer to memory.
Static Memory Allocation – It is known to be the portion of memory for the announced variable by the compiler. The 'address of' operator can be used to get hold of the address which can be allowed to the pointer. At assembly time, memory can be apportioned. In view of the fact that the better part of the declared variables have static memory and looks forward to better management. This type of memory allocation is lain with as static memory allocation.
Dynamic Memory Allocation - This memory gets apportioned throughout the time of execution. The calloc() and malloc() functions hold up the allocation of dynamic memory. Dynamic allocation of memory space can be achievable by means of employing these functions, when it’s worth is brought back by functions as well as apportioned to pointer variables.
Explain Linux Memory Management
Linux is figured out to be a virtual memory scaffold. Virtual Memory introduces a layer of the procedure. With virtual memory, programs keep going the framework can hand out more memory than is bodily easy to get to; even a single process could encompass a virtual address space big as equated to the framework's physical memory. It can be made out realized that the Virtual memory as well countenances the program to participate various tricks with the procedure's address space which lets in mapping out the program's memory to the device memory.
Kernel virtual addresses are like logical addresses as they are representing from the kernel space address to the physical address. Kernel address does not encompass linear mapping to a physical address that represents the logical address space. Every single logical address is kernel virtual addresses, yet plentiful kernel virtual addresses are not said to be the logical address.
Example of kernel virtual address is memory attributed by vmalloc that has a virtual address.
How to Deallocate Memory in C?
This can be very well noticed that the Standard library functions realloc() and free() can be applied so as to deallocate the memory. The following is the assertion of function "realloc()" from "stdlib.h".
void *realloc(void *ptr, size_t size);
In the event that "size" is zero, afterward call to realloc is equal to "free(ptr)". Moreover, if "ptr" is NULL and size is non-zero then call to realloc is indistinguishable to "malloc (size)".
Example of deallocation of memory is
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
int *ptr = (int*)malloc(10);
return 0;
}
Define Computer Memory
Memory serves to be the most important part of PCs that is categorized in a small number of types. Memory is finest storage part to the system clients to keep data, programs and so on, the system memory proffer a few types of storage media some of them can stock up information by the way and some of them can lay up for all time.
Primary Memory/Volatile Memory (RAM) – Similarly, Primary Memory called as volatile memory on the grounds that the memory cannot enduringly store the data. Primary memory is going to decide on any part of memory when client call for to save the data in memory still that may not be stored for all time in that area.
Secondary Memory/Non Volatile Memory - Secondary memory is outer as well as permanent memory that is accommodating to accumulate the external storage media, for example, floppy disk, magnetic disks, tapes etc.
What are Addressing Modes?
Addressing modes serves to be a part of the instruction architecture that stays in most CPU design. The diverse addressing modes that are qualified in an agreed principle, set language directions in that architecture be familiar with the operand(s) of every principle. There are three types of addressing modes:
Register addressing - In this particular mode, the register dwells the operand. Contingent on the direction, the register might be the principal operand, the second operand or both.
Immediate addressing - This operand has the steady value or the expression. At the point when the instruction with two operands uses instantaneous addressing mode, the principal operand might be memory area, and the second operand is a punctual consistent.
Memory addressing - The offset value is decided especially as a main aspect of the guideline, usually established by the variable name. This is acknowledged as direct addressing mode. Indirect addressing is for the most part used for factors comprising a few components such as arrays. The first address of the array economizes in EBX register.
A memory card or flash card is an electronic flash memory data storage device, which is applied for holding open digital data. The TransFlash configuration is one more name for what we now call microSD and they stood electrically the same. Roiand Moreno first made up memory card in 1982.
What is Memory Leak?
Memory leak encounters when the programmer makes a memory in pile and then don't rub out it. This is chief issues for the program like daemons or servers, which never ceases. To preserve a strategic distance from the memory leak, memory attributed on the stack must get dependably be released when didn't really essential. To locate a memory escape, we can have following procedures:
Discover the memory leak – At the first, it is important to detect the existence of memory leak in the framework, given by a detailed reproducible sequence. We ought to have the capability to differentiate a particular procedure.
Separate the memory leak – It is very much needed to settle on the exact area in the source code where the unfreed allotment comes about. This could be a widespread or monotonous process, commanding particular tool, trial–and–error, and cooperation with the first originator of the code.
Remove the memory leak – After the initial two stages are finished, this is effortless. Deciding the memory leak, for the most part, admits contributing some code to open the memory in the code path.
What is Memory Dump?
If Windows blue-screens arise, it brings in memory dump files which are also known as Crash Dumps. This file consists of a duplication of system's memory when it crashes. They can be employed to investigate and tell apart the issue that inspired the crash. Complete memory dump: It is the major kind of large memory dump. This incorporates the copy of the significant number of data employed by Windows as a division of physical memory. If we have 16 GB of RAM and Windows is employing 8 GB during the system crash, the memory dump will be 8 GB in size. By failure to pay, memory dumps are held open at C:\Windows \ MEMORY.DMP. Moreover, the Windows assists to involuntarily remove these files. Disk Cleanup or CCleaner utility automatically deletes all such type of system files.
What is Physical Memory in Operating System?
Physical memory adverts to the authentic RAM of the framework, which comes out as cards (DIMMs) supplemented onto the motherboard. Bluestacks is the most excellent emulator that campaigns all android applications on pc. Bluestacks necessitates graphics card to run Android applications on pc with more than 1 GB RAM. In 1 GB RAM, bluestacks brought in effectively, yet won't give high speed and hangs an extensive measure while playing games. Physical memory is the RAM, and bluestacks commands at least 2GB RAM after the application went authorized.
How to fix Memory Management Error?
The "0X0000001A" error is also anticipated as Memory_Management error and it encounters when the framework memory malfunctions. The total framework memory decreases and the OS contribute to the blue screen error.
Step 1 - When does this error encounters – It seems to be very much decided to take after this well consecrated manual for figure out how to reconcile the blue screen memory management error. This error comes out when your Windows is bringing up in archetypal condition and afterward restarts accordingly.
Step 2 - Open windows in safe mode
Step 3 - Open Control Panel - Keeping in mind the end goal to determine the issue, we should test our RAM.
Step 4 - Open Administrative Tools - In the control board window, open Administrative Tools.
Step 5 - Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool - Accordingly, the Administrative Tools window will open up.
Step 6 - Restart now
What is Contiguous Memory?
If a process demands to perform, memory is invited by the procedure. The measure of the procedure is counterpointed and the measure of contiguous main memory easy to get to execute the procedure. When ample contiguous memory is bumped, the procedure is dealt memory to start in on its execution. Else, it is increased to line up for holding up procedures until enough free contiguous memory is easily reached.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Question
What is memory management blue screen?
Answer
When the computer stops functioning, or system has been furnished been usable by MEMORY_MANAGEMENT error, a blue screen comes along.
Question
What is peripheral management?
Answer
Peripheral management controls an assortment of peripherals devices by broadcasting commands in their own coding languages.
Question
What is contiguous memory allocation in operating system?
Answer
Contiguous memory allocation seems to be the memory allocation model that apportions the process to memory blocks.
Question
What are different types of memory management in operating system?
Answer
1. Single next-door allocation
2. Partitioned allocation
3. Paged memory management
4. Segmented memory management
Question
What are different types of Cache memory?
Answer
1. Level 1 (L1) Cache
2. Level 2 (L2) Cache
3. Level 3 (L3) Cache
Question
What are different levels of Cache memory?
Answer
1. Level 1 (L1) Cache
2. Level 2 (L2) Cache
3. Level 3 (L3) Cache
Question
What is cache memory in mobile?
Answer
In mobile phones, cache touches to a memory storage area in the telephone or network that store copies of data which can be expended in the future course of time.
Question
Why is cache memory needed?
Answer
The cache memory lays in the program as of now being performed or which might be executed surrounded by a concise timeframe.
Question
What is virtual memory paging?
Answer
Virtual memory is by and large carried out by demand paging. It can likewise be substantiated in a segment system.
Question
What is the virtual memory in computer architecture?
Answer
In computer architecture, virtual memory is a memory management strategy that is substantiated employing both hardware as well as software.
Question
What are advantages of virtual memory?
Answer
The main gain or goal of Virtual Memory frameworks is the capability to load and implement a procedure that necessitates a measure of memory than what is reachable by loading up the procedure in parts and after that carrying out them.
Question
How to allocate memory in C++?
Answer
We can very well assign memory at runtime in the heap for the variable of known type by means of employing a special operator new in C++ which returns the address of the space circulated.
Question
How to measure actual memory usage in Linux?
Answer
Valgrind can illustrate the amount of memory which is applied, and various memory leaks in the program.
Question
What is the purpose of Linux free command?
Answer
A free command in Linux is used to make available the element about habituated as well as unused memory as well as swap spaces on the system that campaigns Linux.
Question
What is Linux cached memory?
Answer
The Linux cached memory is extremely invisible. It can be seen that it uses unused memory to unusually disk access speeds, and without getting rid of any memory from applications.
Question
How to check CPU in Linux?
Answer
Answer
Lscpu, /proc/cpuinfo and I stop (HELOC)
Question
How to check disk space in Linux?
Answer
Df, du command
Question
What is the return type of calloc()?
Answer
Void
Question
How to deallocate memory in C++?
Answer
Delete(), free()
Question
What are different types of memory in the computer?
Answer
Volatile (DRAM, SRAM)
Non-volatile (ROM, PROM, EPROM, EEPROM)
Question
What are the stages of memory?
Answer
Encoding information, Storing information, Retrieval information
Question
What is indexed addressing mode?
Answer
Indexed addressing Mode is employed to entrée an array whose components are in progressive memory areas.
Question
What is direct addressing mode?
Answer
Direct addressing mode incriminates that the value for a given instruction in assembly programming is pointed by a given value.
Question
What is indirect addressing mode?
Answer
This mode employs a register to grasp the real address that keys out either the source or the goal to be employed as a part of the data move.
Question
What are different addressing modes of 8085?
Answer
Immediate addressing, register addressing, direct addressing, indirect addressing
Question
What is relative addressing mode?
Answer
The PC-relative addressing mode can be employed to pack a register with a worth which is stored in program memory a short distance far from the present instruction.
Question
What is the immediate addressing mode?
Answer
When the instruction with two operands utilizes immediate addressing mode, the principal operand might be memory area, and the second operand is a prompt consistent.
Question
What is T flash card?
Answer
The TransFlash configuration is another name for what we now call microSD
Question
Who made the first flash card?
Answer
Roiand Moreno
Question
How much is an SD card?
Answer
$15
Question
What are different types of memory card?
Answer
Secure Digital card (SD)
· MiniSD Card with an SD card adapter.
· CompactFlash (CF-I)
· Memory Stick.
· MultiMediaCard (MMC)
· SmartMedia.
· xD-Picture Card.
Question
What is the memory leak in c++
Answer
Memory leak encounters when the programmers make a memory in stack and then don't remove it.
Answer
By registry hack
Fix the driver issue
Adjust windows 10 for best performance
Question
How to detect memory leak
Answer
In Windows 7, right-click the taskbar of Windows and select Task Manager. Alternately click the Start button and type "Task Manager" in the search box. After that, click the Performance tab. We will make out boxes for the CPU and Memory.
Answer
By writing a library using JNI.
Question
What is a memory dump file?
Answer
The file formats where debug information can be composed to different file formats.
Answer
It contains knocked down data from program memory space.
Answer
It is computer’s documented memory when a system crashed.
Question
What is the location of dump file?
Answer
C:\Windows\MEMORY.DMP
Answer
BlueScreenView utility
Question
How to read dump files windows 10?
Answer
WinDBG
Answer
It comprises the copy of the significant number of data used by Windows as a part of physical memory.
Question
What is the physical memory in Bluestack?
Answer
Minimum 2GB RAM
Question
How do i free up memory on my computer?
Answer
The most natural approach to liberate RAM being used is to open Windows Task Manager. Discover to the Processes tab and after that sort the list of open programs by memory. This will make known any procedure that is consuming a strangely extensive volume of RAM.
Question
What is linked allocation?
Answer
Where each file is linked list of disk blocks.
Question
What are advantages of contiguous memory allocation?
Answer
Question
What is the disadvantage of contiguous memory allocation?
Answer
The degree of multiprogramming is reduced because of processes that wait for free memory
If you need more help in memory-management-homework-help
Click here